Mushrooms have been used as food with various health benefits worldwide. Edible species of mushrooms are cultivated throughout the world at the commercial level. These mushrooms are also collected in the wild during the rainy season as food. Pleurotus is the world’s second most cultivated and popularly consumed edible mushroom due to its unique texture, taste, and food content. It is enriched with carbohydrates, proteins, ash, fats, fiber, mineral elements, and important amino acids. Pleurotus ostreatus is a good source of proteins, fibers, and carbohydrates, with low contents of fats and few metals contents. In cultivated Pleurotus ostreatus amino acids like glutamic acid and aspartic acid were found in higher quantities. It is used as a protein-rich food with many health benefits worldwide (Bano et al., 1988).
Edible mushrooms are the best source of food due to their high contents of proteins, low amount of fats and essential nutrients, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus with vitamin D and B. Fatty acids like linoleic acid, oleic acids, and palmitic acid are also found in edible mushrooms (Kalac et al, 2013).
Wild edible mushrooms have low contents of saturated fats and higher contents of proteins and fibers. They might reduce the blood cholesterol level and lower the risk of heart attack (Eva Guillamón et al., 2010)
Edible mushrooms like Boletus edulis, Lactarius deliciosus, and Suillus collinitus contain a valuable number of organic acids and other food elements. Common organic acids isolated from the samples were malic acid, Fumaric acid Succinic acid, and citric acid, (Valentao et al., 2005). Edible mushrooms are praised throughout the globe for their nutritive and therapeutic benefits, phenolic and bioactive compounds having medicinal and food value. Mushrooms have a good profile of nutrients, organic acids, vitamins, other antioxidants, and antitumor compounds (Harpreet Kour et al., 2022).
Edible mushrooms contain essential amino acids and other vitamins. Mushrooms are gaining importance by researchers worldwide due to their nutritional and pharmacological importance. Biomolecules of mushrooms have good biological and medicinal potential against different diseases. Recently mushrooms have gained the attention of the scientific community due to their nutritional value and high profile of proteins (Irene Roncero-Ramos & Cristina Delgado-Andrade, 2017).
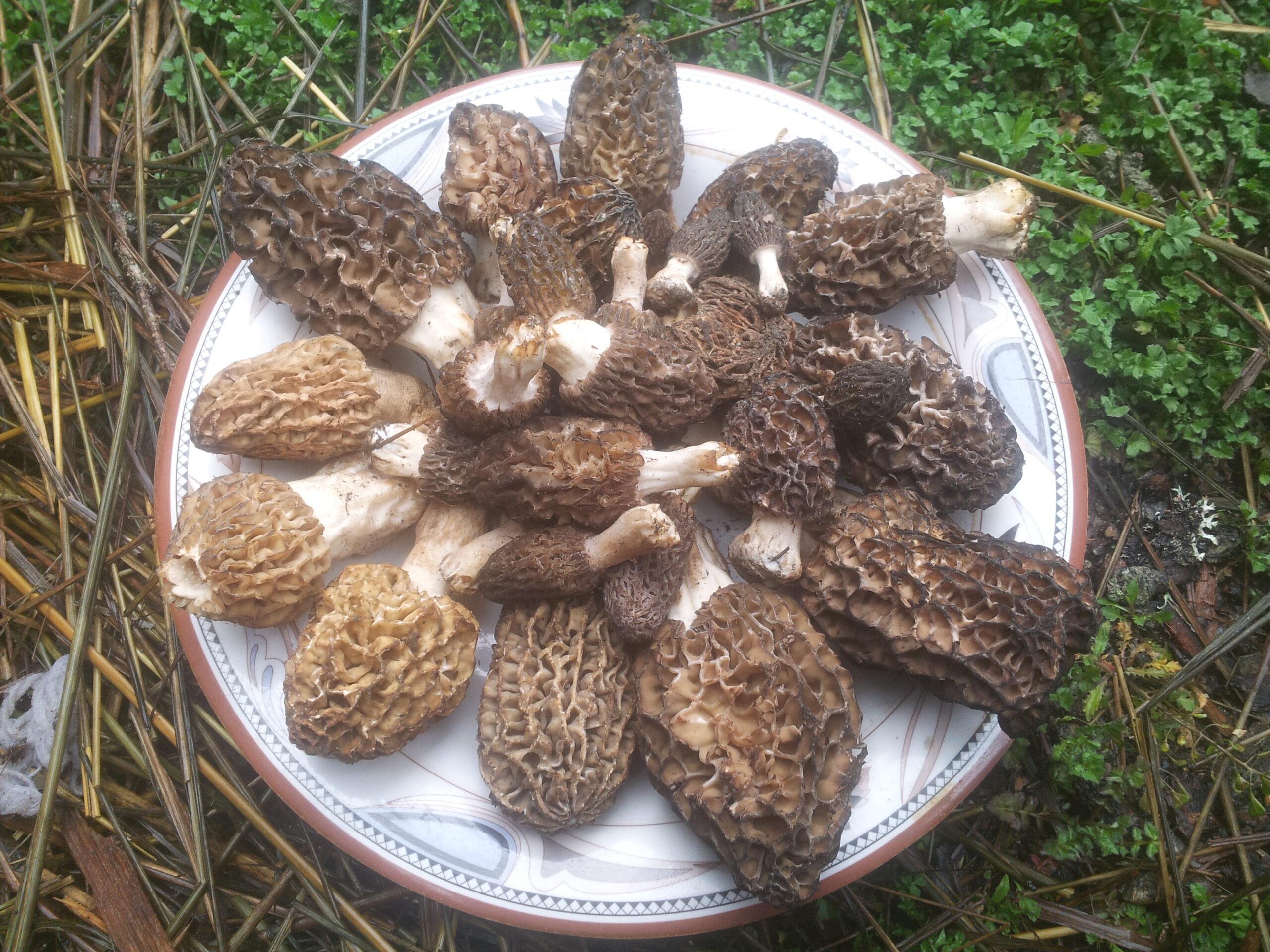
Edible mushrooms, Sparassis crispa, Polyporus squamosus, Coprinopsis cinerea, and Boletus edulis have been cultivated and used as a good source of secondary metabolites and phenolic compounds (Chopra et al., 2021). Morels, Morchella esculenta, M.conica, M. elata, M. deleciosa are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, carbohydrates, and bioactive compounds (Tietel & Masaphy, 2017).
Different low molecular-weight bioactive compounds were isolated from the mushrooms like anthraquinones, sesquiterpenes, quinolines, and oxalic acid. These compounds have been reported to have good antimicrobial activity and anti-aging agents and stress (Loftus et al., 2020).
Wild edible mushrooms are also considered rich sources of minerals elements like Ca, Si, K, Se Mg, and Si which contribute to health improvement. All these minerals are detected with very low concentrations in different mushroom species. The mineral profile of these mushrooms suggests that they are a good source of food content (Sezgin et al., 2019).